Using advanced search
DailyStory's search capabilities include some advanced options to help you narrow down your results to build advanced segments.
Wildcards for matching multiple results
Wildcard search is an advanced search technique that can be used to maximize your search results in DailyStory’s contact database. To do a wildcard search, apply any of the following methods:
- Add an asterisk (*) at the end of a partial keyword or a group of characters if you want to pull up results that match the word or characters you entered prior to the asterisk. For example, if you search for
Rob*, the search will return a list of contacts that may have Roberts, Robertson, or Robinson as part of their data in DailyStory. The asterisk will allow for an infinite number of characters in the search as long as the first few characters you specified remain the same.
Make sure that you place the asterisk at the end of your text. Adding the asterisk before your keyword or characters does not qualify as a wildcard search.
- Add a question mark (?) at any position of your keyword to indicate that you are missing a character and want to pull up results that may match the missing character. Note that a single question mark symbol represents one missing character. For example, if you search for
J??n, the search will return a list of contacts that may have John, Joan, or Jann as part of their data in DailyStory.
It's also to important to remember that when using direct search, versus searching within a field, the search will match across all fields. For example a search for rob* will match on first name, last name, etc.
Search for an exact phrase
To search using a phrase, enclose your keywords with double quotation marks. For example, use “Gold Weekly Members”. This will only match records that have that exact phrase. Whereas the same search without quotes will match any occurrence.
Exclude results from search
Add a minus sign (-) before the text or information you don’t want to be used as a search criteria. For example, use John -Smith as your search text if you want to find contacts whose first name is John but don’t have Smith as a last name.
Exclusion matching gets complex quickly, especially if there are multiple constraints. It's easiest to create a new segment with all the criteria used for the exclusion and then simply use that segment as an excluded segment.
Find multiple matches in the same field
When you’re filtering your search using contact fields that accept text array value, you can use more than one piece of data as the search criteria.
For example, if you want to search using multiple postal codes, enter the postal codes and separate each code with a comma.
Search using date periods or ranges
Contact fields that are configured to accept date periods or ranges enable you to narrow down your results to a specific time window.
For customers using integrations such as Shopify, or other ecommerce integrations, it's common to want to build segments such as: customers that have not ordered in past 45 days.
These types of ranged based segments are automatically included when these integrations are enabled. However, you may want to build your own ranges or customize and existing range based search. Therefor, it's import to understand how they work.

When using a date field there are several options you can toggle between range and period input as preferred to specify your search criteria:
Range-based search
Range-based search is the default search option presented. It allows searching for results between two specific dates, such as August 1, 2025 and August 31, 2025.
Period-based search
Clicking the Period option changes the search to a simple sliding period of time, e.g. previous 30 days or next 1 month. This date is always relative to the current date.
When the period uses previous the date to will be today. When the period uses next the date from will be today.
Preset search
The preset search option includes some pre-configured and common searches, such as between 30 and 60 days ago.
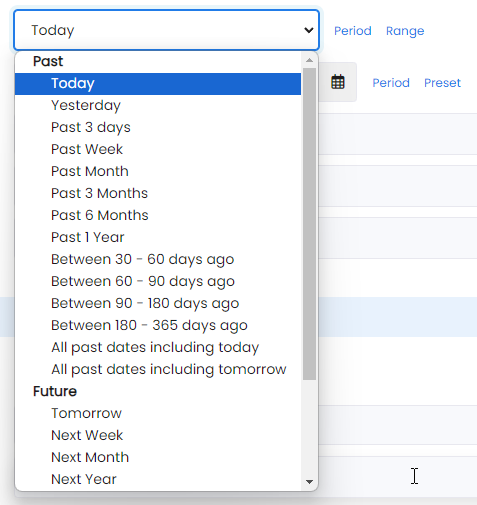
While complex, this enables very robust search options. For example, between 30 and 60 days ago only includes dates calculated as "today's date minus 30 days and today's date minus 60 days".
If today's date is August 30, 20205 this would return results that were between July 1 and July 31.
RecommendedA period-based search gives you more flexibility as it enables you to search using a specific time window, such as the next 30 days or the past 15 days.
Sliding versus fixed dates
When a period search is performed instead of passing exact dates in the URL special tokens are set to allow search to calculate the date each time search is run. This enables date ranges that are variable based on the current day.
For example, if today is August 7, 2025 a search with the value "yesterday" will return results for August 6, 2025. However, on August 8, 2025 the results will be for August 7, 2025. While dates can get complicated, sliding date windows enable some powerful segments.
Sliding date values and syntax
Below are the values
Dynamic dates
DailyStory support dynamic range searches (as described above in Birthdays today, tomorrow and other ranges). Below are the supported range criteria.
| yesterday | When comparing dates, use yesterday's date. For example, if today is June 15, 2023 yesterday is June 14, 2023. |
| today | When comparing dates, use yesterday's date. For example, if today is June 15, 2023 today is June 15, 2023. |
| tomorrow | When comparing dates, use yesterday's date. For example, if today is June 15, 2023 tomorrow is June 16, 2023. |
| next-N-days, next-N-weeks, next-N-months, next-N-years | Used to built dynamic search ranges. For example, if today is June 15, 2023 and we wanted to match on any date in the next 15 days: next-15-days. |
| past-N-days, past-N-weeks, past-N-months, past-N-years | Used to built dynamic search ranges. For example, if today is June 15, 2023 and we wanted to match on any date in the past 15 days: past-15-days. |
For example, to find contacts with birthdays in the next week using the following search:
$dateBirthFrom=today&dateBirthTo=next-1-week
Working with Birthdays and Age
DailyStory maintains and updates the annual birthday for your members (if you have provided their date of birth).
A common request may be to build a segment for everyone whose birthday is in June (or any other month). However, this can be problematic since the birth year can vary. For example, if today is May 3rd, 2026 and two member's birthdays are June 29, 1983 and June 7, 1974.
Special anniversary date
DailyStory solves this by constantly updating a contact's birthday to their next anniversary date. In this case, June 29, 2026 and June 7, 2026.
While specifying the exact dates for your birthday search may work in some cases, a more powerful option is to use a period search, e.g. birthdays within the next 3 days. When used in a dynamic segment it will constantly update each day as the criteria changes.
For a shortcut for common searches, type the following searches into the DailyStory search:
- Birthdays today - &dateBirthFrom=today&dateBirthTo=today
- Birthdays tomorrow - &dateBirthFrom=tomorrow&dateBirthTo=tomorrow
- Birthday in next 3 days - &dateBirthFrom=today&dateBirthTo=next-3-days
Contact Age
The contact's age is a special field available in search. It is a calculated field based on the contact's date of birth and the current date. This field is recalculated each time a contact is updated in search. All contacts are assigned an age of 0 if no date of birth is provided. And, a maximum age of 100 if the date of birth is more than 100 years ago.
This enables search where the ageTo=18 that would include anyone with is 18 years old or younger and people that do not have a date of birth.
Search for contacts by email address
The search section Filter by email address enables searching and segmenting contacts based on various details regarding their email address.
Search for a specific email address
The first option, Email, enables searching for a specific email address. This is most useful when looking for a specific contact. You can include a list of up to 25 email address separated by a comma and use wildcard options to search for specific matches. For example, find people that have the name James: james*. This would match jamesj@example.com, james@exmample.com, etc.
Search by email domain
This enables searching for contacts that match a specific email domain. For example, if you wanted to find all contacts with a nasa.gov email address.
Multiple domains can be entered. For example, find all hotmail.com and gmail.com email addresses. You can also select from pre-set options from the provided picklist or enter your own.
This field is configured as a pick list with some pre-set options, such as Gmail, Yahoo, Outlook, etc. Below are the domains included for each pre-built picklist option:
| Friendly name | Included domains |
| Gmail | gmail.com, googlemail.com |
| Outlook / Hotmail / Live | outlook.com, hotmail.com, live.com, msn.com, windowslive.com |
| Yahoo / Ymail | yahoo.com, ymail.com, rocketmail.com |
| iCloud / Me / Mac | icloud.com, me.com, mac.com |
| Apple Private Relay | privaterelay.appleid.com |
| Comcast / Xfinity | comcast.net, xfinity.com |
| Verizon | verizon.net;verizon.com |
| AT&T / SBC Global | att.net, sbcglobal.net, bellsouth.net, ameritech.net |
| Spectrum / Charter | charter.net, spectrum.com, twc.com, roadrunner.com |
| Cox | cox.net |
| AOL | aol.com, aim.com |
| Proton Mail | proton.me, protonmail.com, pm.me, duck.com, tuta.com |
| Free / Anonymous | mailinator.com, 10minutemail.com, guerrillamail.com, temp-mail.org |
Search by email TLD (Top Level Domain)
The email TLD (Top Level Domain) enables searching for contacts that match a specific TLD (e.g., gov or edu). For example, if you wanted to find all contacts associated with a .gov email address.
Multiple TLDs can be entered. For example, find all .gov and .edu email addresses. You can also select from pre-set options from the provided picklist or enter your own.
Below is an example of a search for emails that end in the TLD .edu:
 Important
ImportantWhen entering your own TLD do not include the period. For example, gov instead of .gov.
This field is configured as a pick list with some pre-set options, such as com, org. net, etc. Below are the TLDs included for each pre-built picklist option:
| Friendly name | Included TLD |
| Business (.com) | com |
| Non-Profit/Org (.org) | org |
| Network (.net) | net |
| Government (.gov) | gov |
| Education (.edu) | edu |
| Military (.mil) | mil |
| Technology (.io, .ai, .tech, .dev, .app) | io, ai, tech, dev, app |
| Corporate/Global (.co, .biz, .inc, .llc) | co, biz, inc, llc |
| North America (.us, .ca) | us, ca |
| United Kingdom (.uk) | uk |
| Europe (.eu) | eu |
Geographic search for contacts
DailyStory includes powerful geo-based search for building segments based on the geographic location of contacts (their specific latitude and longitude position).
How are contacts geo-coded?
Contacts can be geocoded in several ways:
- Automatically - many of the native integrations will automatically attempt to geocode records as they come into the system, such as Shopify integration. However, this automatic geo-coding is not as specific vs. using Google's maps API.
- Google Maps API - by providing a Google Maps API key DailyStory will fetch highly accurate geo-coding data for a given address. However, there are fees associated with using Google Maps.
- Self-code - customers may also optionally provide the latitude and longitude for records imported into DailyStory.
Once an address is looked up via a geo coding service, that address's latitude and longitude is stored by DailyStory. Thus if using Google Maps API you will only ever pay to lookup an address one time.
Once geo-coded you can provide your own address, such as your store's address, and specify a radius to include. For example, if your store is in Salt Lake City, Utah you can provide the exact address and range bound the results to anyone within a 15 mile radius.
If you only provide a city, the range will be centered from the center point of the city.
Search by zip or postal code
The Postal Code field is used to find contacts with a specific postal code (zip code). Enter one postal code or enter multiple postal codes separated by a semi-colon or comma.
Search by area code
Navigate to the Mobile Phone field and enter +1 and then the three digit area code, followed by a * (an asterik) Be sure there are no spaces. Example: To search for all contacts with an 816 area code, you would type +1816* in the mobile phone field.
Search by Campaign Engagement
This search section contains multiple options for finding contacts based on interactions with various campaigns. For example, contacts within specific campaigns, contacts that are part of (or not part of) specific segments
Using AND and OR syntax
DailyStory supports searching using logical operators, such as AND and OR.
- Use OR if you want to retrieve results which contain any of your specified search criteria. For example, use
Dallas OR Austinto search for contacts that may be located in either one of the specified cities. - Use AND if you want to retrieve results which contain all of your specified search criteria. The AND command ensures a more accurate list of results for your search. For example, use
Company A AND Company B AND Company Cto search for contacts that are associated with all of the specified organizations.
Advanced Exclusion Filtering
Several search options exist in DailyStory for fields such as segments and tags that allow for exclusion filtering. For example, trying to build a segment while excluding other segments.
To return contacts that are in segment id 567 and 890:
segments=567,890
Including a negative symbol in front of this:
-segments=567,890
Says to exclude contacts from results if they are in segment 567 OR segment 890.
However, you may want to instead exclude contact if they are in segment 567 AND segment 890.
This can be accomplished by adding :all after the name of the field:
-segments:all=567,890
Exclusion Filtering Syntax
| Example | Explanation |
segments:any=567,890 | Return contacts that are in any of the listed segments. Equivalent to: segments=567;890. |
-segments:any=567,890 | Returns contacts that are not in segment 567 OR segment 890. Equivalent to:-segments=567,890 |
segments:all=567,890 | Returns contacts that are in segment 567 AND segment 890. |
-segments:all=567,890 | Returns contacts that are not in segment 567 AND segment 890. |